Update the Express service to use the Aserto Express.js middleware
In order to have our policy govern authorization in our service, we need to configure and apply the Aserto Express.js middleware. In order to avoid saving any secret credentials in our source code, we'll add the following credentials to our .env file. To find these credentials, click the aserto-react policy instance the Policies tab, then choose the "Settings" tab.
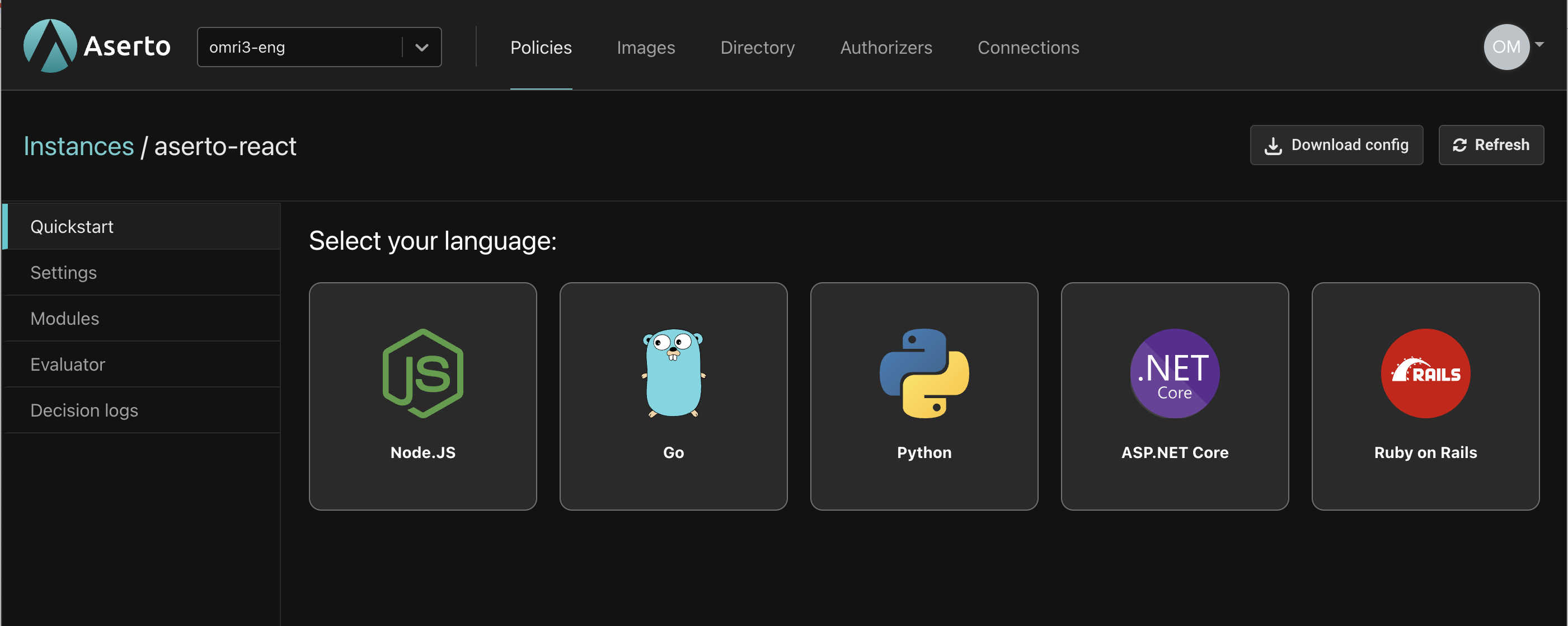
Click the "Download config" button in the top right, and add the values in the downloaded file to your .env file:
ASERTO_POLICY_INSTANCE_NAME=aserto-react
ASERTO_POLICY_INSTANCE_LABEL=aserto-react
ASERTO_TENANT_ID={Your Tenant ID}
ASERTO_AUTHORIZER_API_KEY={Your Authorizer API Key}
ASERTO_AUTHORIZER_SERVICE_URL=authorizer.prod.aserto.com:8443
ASERTO_POLICY_ROOT=asertodemo
In the service directory, install the @aserto/aserto-node package:
yarn add @aserto/aserto-node
Then, add the following dependency reference in service/api.js (after the const jwt = require("express-jwt"); line):
const { jwtAuthz } = require("@aserto/aserto-node");
Continue by creating the configuration object for the Aserto middleware. Add the following section after the const app = express(); line:
const authzOptions = {
authorizerServiceUrl: process.env.ASERTO_AUTHORIZER_SERVICE_URL,
instanceName: process.env.ASERTO_POLICY_INSTANCE_NAME,
instanceLabel: process.env.ASERTO_POLICY_INSTANCE_LABEL,
policyRoot: 'asertodemo',
authorizerApiKey: process.env.ASERTO_AUTHORIZER_API_KEY,
tenantId: process.env.ASERTO_TENANT_ID,
};
We'll define a function for the Aserto middleware, and pass it the configuration object.
//Aserto authorizer middleware function
const checkAuthz = jwtAuthz(authzOptions);
Lastly, add the checkAuthz middleware to our protected route: Add the reference to the checkAuthz middleware right after the checkJwt middleware reference. You endpoint definition should look like this:
//Protected API endpoint
app.get('/api/protected', checkJwt, checkAuthz, function (req, res) {
//send the response
res.json({ secret: 'Very sensitive information presented here' })
})
The checkAuthz middleware is going to pass the request context - which consists of the policy reference (based on the request route), the identity context (based on the JWT token passed) and resource context (based on the request parameters) - to the authorizer, which given the policy will determine what the allowed decision would be.
Test the Application
Before testing the application, stop both the application and the server by hitting ctrl+c and run yarn start:all again.
When we log in with the user krisj@acmecorp.com who has the role of an admin we will still be able to see the following:
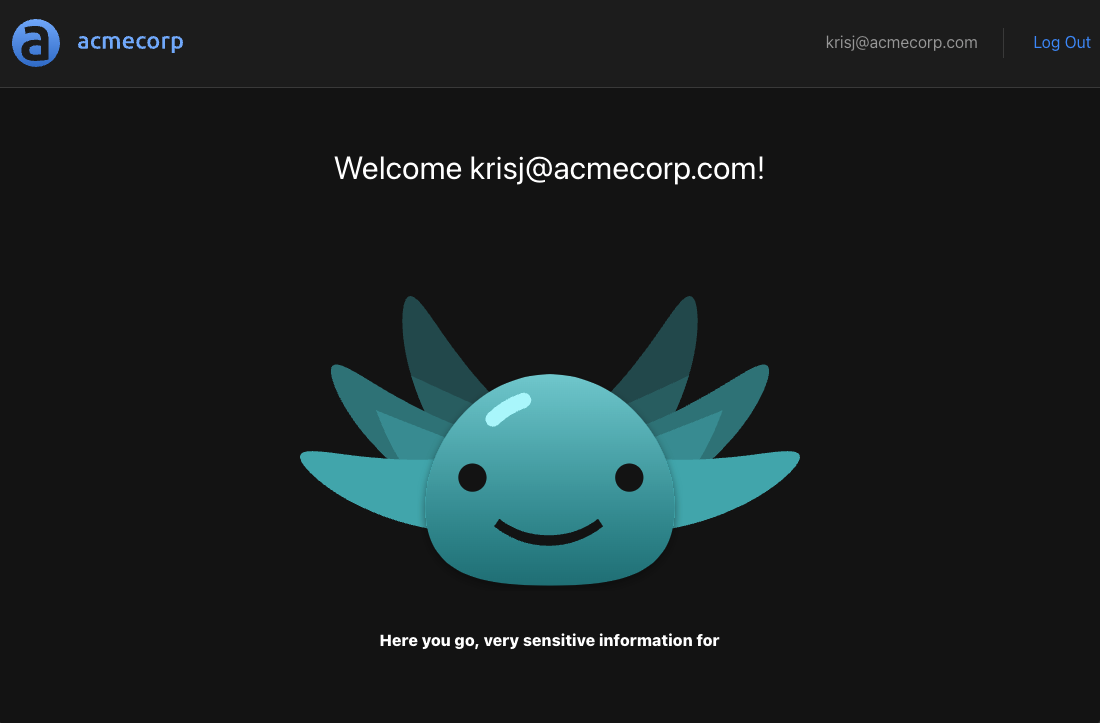
If we log out and log in again as euang@acmecorp.com we will see the following:
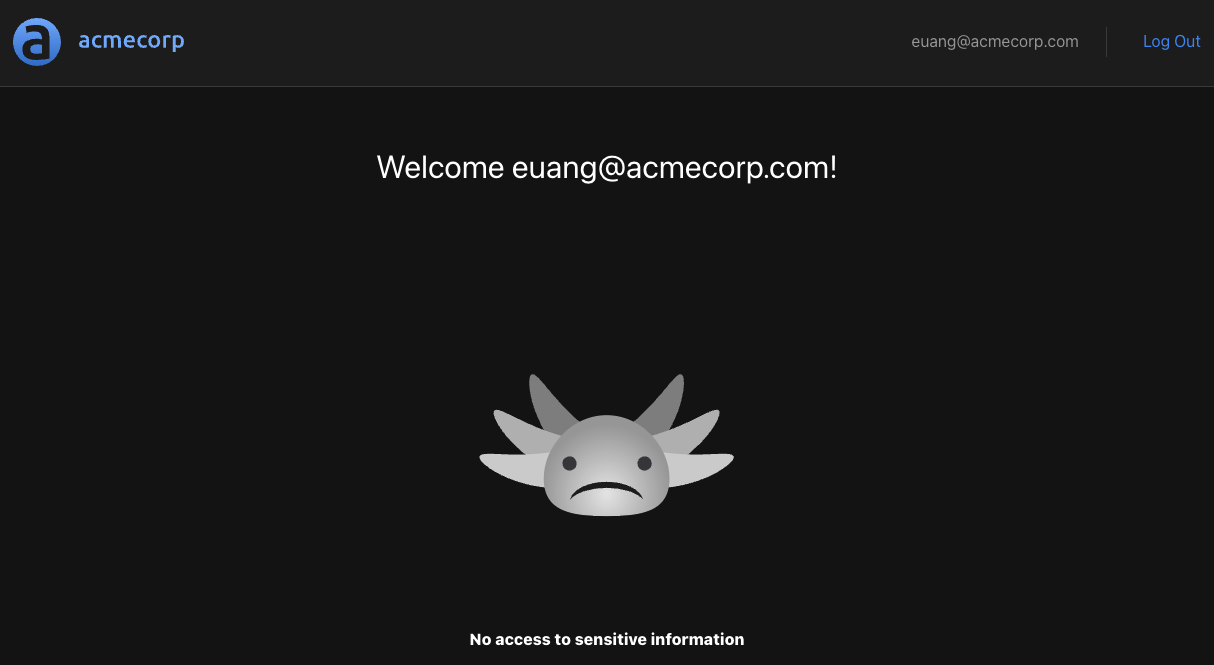
Euan doesn’t have the role of admin, and the route /api/protected will be disallowed.
Checkpoint
We have successfully set up an endpoint that is protected by two middleware functions: checkJwt which validates the JWT token, and checkAuthz which validates that the logged in user's role is allowed access to the endpoint. But right now, our policy is very limited - it only has a single role (admin). In the next section we'll learn how to expand our policy to include more roles.