Architecture
Aserto has two major components:
- Authorizer: where authorization decisions are made.
- Control Plane: manages all the artifacts that the Authorizer uses to make authorization decisions.
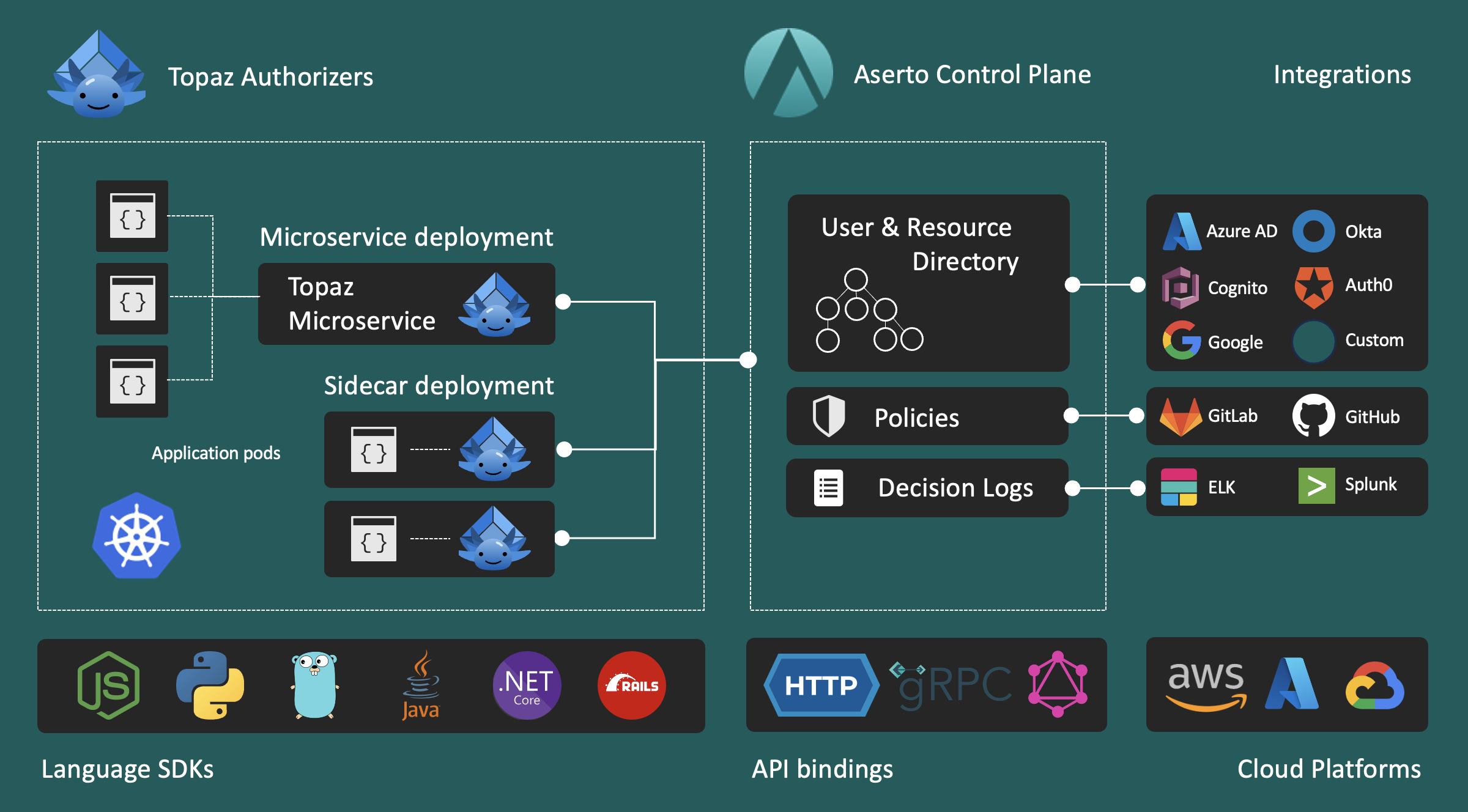
Authorizer
The Authorizer is the component that makes authorization decisions based on inputs. Aserto leverages the Topaz open source project as its Authorizer. Topaz, in turn, leveragess the CNCF Open Policy Agent (OPA) engine to compute a decision based on a policy, user context, and resource data. The Authorizer is most commonly deployed close to your application, to offer the lowest latency and the highest level of availability to your application.
Authorization requires both rules (logic) and data (properties about subjects, objects, and relationships between them). OPA handles the logic, but doesn't help with data. Topaz adds a "data plane" to OPA, in the form of an embedded database that caches all the data that's needed for authorization decisions. This data is sourced from the Aserto Directory, which is inherits its design from Google's Zanzibar system.
Control Plane
The Aserto Control Plane manages the lifecycle of policies, user context, and resource data that are used by the authorizer. The Control Plane makes it easy to manage these artifacts centrally, and takes care of the details of synchronizing them to the Authorizer instance(s) deployed at the edge.
The Control Plane also aggregates all of the outputs from the Authorizers, including decision logs, to give an administrator a centralized, single-system view of a complex distributed system.
Next Steps
If you're new to authorization, check out the Authorization Basics topic to learn more about the differences between AuthN and AuthZ, and also about the various styles of authorization.
You can learn more about the differences between Topaz and Aserto.
Otherwise, let's dive deeper into the Aserto Concepts.